A multicooker pot with advanced composite bottom design promotes energy efficiency and safety. The design distributes heat evenly, which improves quality and protects food. Composite bottom design also increases energy efficiency. High-quality materials raise safety levels. Energy efficiency, safety, and quality depend on the design and construction of each multicooker pot.
The Science Behind Multicooker Pot Materials
Heat Conductivity and Distribution
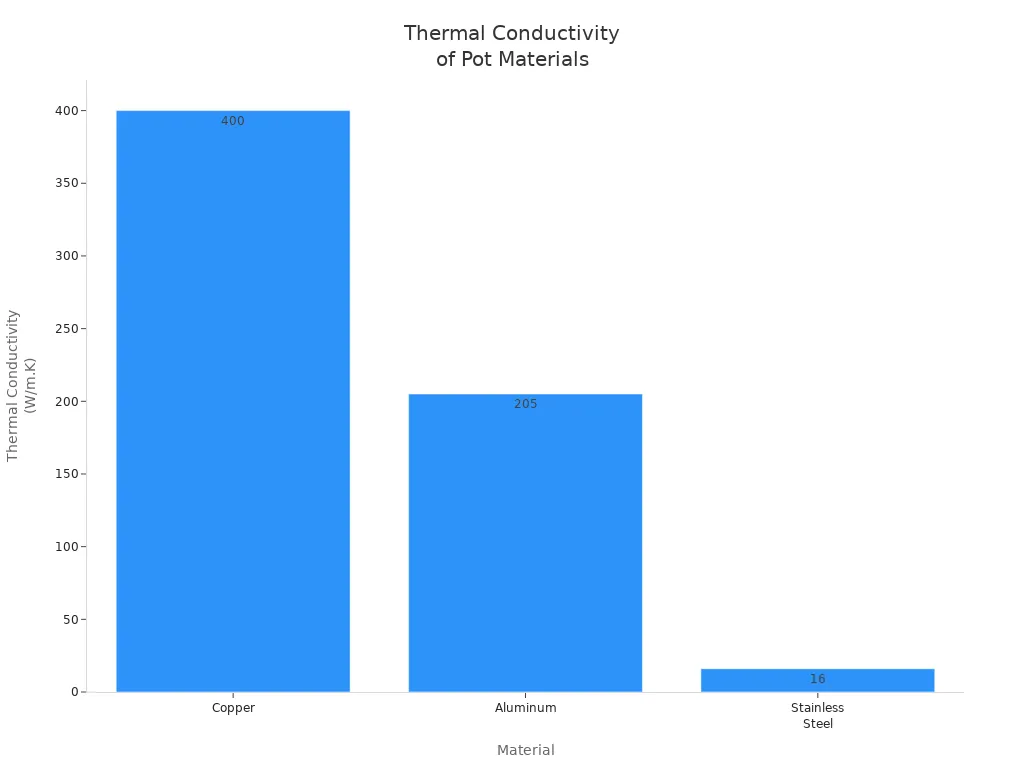
Material selection plays a vital role in how a multicooker manages heat. Each material has a unique ability to conduct and distribute heat, which affects cooking quality and energy use. The scientific principle of thermal conductivity explains these differences. Metals like copper and aluminum have high thermal conductivity, which means they transfer heat quickly and evenly. Stainless steel, while popular for its durability, has lower conductivity and can create uneven heating unless combined with other metals.
| Material | Thermal Conductivity (W/m.K) | Key Heat Conductivity Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Copper | ~400 | Very high conductivity; allows precise temperature control |
| Aluminum | ~205 | Moderate conductivity; lightweight and good heat conductor |
| Stainless Steel | ~16 | Low conductivity; uneven heat distribution unless layered |
| Cast Iron | N/A | Retains heat well but not known for high conductivity |
Multi-layer bases with encapsulated aluminum cores have become the industry standard for uniform heating. These designs use 3-5 layers of high-efficiency heat-conducting materials, such as aluminum, stainless steel, and sometimes copper. This approach ensures rapid, uniform heat conduction and prevents hot spots. Uniform heating improves food quality and reduces energy waste. Induction-compatible pots also use these layers for better efficiency and precise temperature control.
| Pot Material | Heat Distribution Uniformity | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | May have uneven heat distribution | Durable, versatile, easy to clean | Uneven heat distribution, higher power use |
| Non-Stick | Can suffer from uneven heat distribution | Easy to use, effortless cleanup | Coating degradation, uneven heating |
| Induction-Compatible | Rapid and even heat distribution | Energy-efficient, precise temperature control | More expensive, requires compatible cookware |
| Ceramic | Even heat distribution | Energy-efficient, non-stick surface | Limited max temperature, less versatile |
| Multi-Layer Coating | May experience uneven heat distribution | Combines non-stick and heat resistance | Coating wear over time |
Material selection for the pot base and walls directly impacts quality, safety, and energy efficiency. Choosing the right combination of stainless steel and aluminum layers ensures uniform heat conduction and better cooking results.
Durability and Longevity
Durability stands as a key factor in material selection for multicooker pots. Manufacturers use laboratory tests to measure how well each material withstands pressure, heat, and repeated use. These tests include heat exposure, physical stress, pressure, sealing, fatigue, and food contact migration. Each test checks for flaws that could affect safety or quality.
| Test Type | Purpose / What it Measures |
|---|---|
| Heat Exposure Test | Assesses heat tolerance and durability under cooking heat |
| Physical Stress Test | Evaluates resistance to mechanical stress and wear |
| Pressure Test | Checks structural integrity under pressure conditions |
| Sealing Test | Ensures lid and pot sealing durability and safety |
| Fatigue Test | Simulates repeated use to detect material fatigue |
| Food Contact Migration Test | Detects harmful substance migration into food, ensuring chemical safety |
Stainless steel pots often last for decades with proper care. Aluminum pots, while lightweight, may warp or wear out faster under pressure. Nonstick coatings can degrade over time, especially if exposed to high pressure or metal utensils. The average lifespan of each material depends on quality, usage, and adherence to strict manufacturing standards.
| Material | Average Lifespan Under Typical Usage Conditions |
|---|---|
| Nonstick cookware | 2 to 10 years depending on quality |
| Stainless steel | Decades of constant use |
| Copper | Lifetime (may require relining every few decades) |
| Carbon steel | Lifetime with proper care |
| Cast iron | Decades to lifetime |
| Ceramic | Less than 5 years |
Material selection based on durability ensures long-term safety and consistent quality, especially when the pot must withstand repeated pressure cycles.
Food Safety and Non-Reactivity
Food safety remains a top priority in material selection for multicooker pots. Stainless steel stands out as the most resistant to leaching and chemical reactivity. It does not react with food and resists wear, making it ideal for health-conscious users. Ceramic and glass also offer non-reactive surfaces, but ceramic may leach lead if damaged or poorly made. Titanium provides complete inertness but is less common in multicookers.
- Stainless steel (especially 18/8 or 18/10 grades) resists leaching and chemical reactivity.
- It is non-reactive, free from toxic coatings, lead, PFAS, and aluminum, and highly durable.
- Stainless steel may leach trace amounts of nickel or chromium under acidic conditions and long cooking times, but this is minimal and generally safe.
- Ceramic materials are non-toxic alternatives but carry risks of lead leaching if damaged or improperly manufactured.
- Ceramic non-stick coatings can expose aluminum cores that may leach into acidic foods.
- Titanium cookware is completely inert and non-reactive, potentially safer than stainless steel, but less common in slow cookers.
- Glass is safe and non-reactive, preventing harmful substances from leaching.
- Glazed ceramics and non-stick coated inserts containing PFAS/PTFE should be avoided due to leaching risks.
Manufacturers must follow strict manufacturing standards and international safety standards to ensure material safety. The LFGB certification, a German food safety standard, applies to multicooker pots. This certification checks for chemical hazards, migration of substances, and heavy metal content. The knife and fork logo on a product signals compliance with these standards, ensuring the pot meets high expectations for safety and quality.
Note: Material selection affects not only cooking performance but also the health and safety of everyone using the multicooker. Always check for certifications and choose pots made from high-quality, non-reactive materials.
Common and Advanced Multicooker Pot Materials in 2025

Stainless Steel
Stainless steel remains a top choice for multicooker pots in 2025. Many users prefer high-quality stainless steel because it offers durability and corrosion resistance. Stainless steel does not react with food, so it keeps flavors pure and safe. Cleaning is easy, and the material supports adjustable pressure settings for different recipes. Manufacturers often combine stainless steel with nonstick coatings, making the pot more versatile and easier to maintain. Safety features like overheat protection and advanced pressure release devices work well with stainless steel pots, supporting multi-functionality and user safety.
- Stainless steel inner pots provide long-lasting performance.
- The material is non-reactive and easy to clean.
- Stainless steel supports advanced safety features and versatile cooking.
Aluminum and Anodized Aluminum
Material selection often includes aluminum for its excellent heat conductivity. Standard aluminum is lightweight but can scratch or warp. Anodized aluminum, however, has a hardened surface created by an electrochemical process. This surface resists scratches, chipping, and corrosion. Anodized aluminum does not react with acidic foods, so it is safer for cooking. It also maintains its shape under high heat and lasts longer than standard aluminum. Many multicooker pots now use anodized aluminum for better safety and durability.
Nonstick Coatings and Innovations
Nonstick coatings have seen major advances in 2025. Manufacturers use nanotechnology-based coatings, sol-gel coatings, and graphene-enhanced coatings to improve durability and safety.
| Coating Innovation Type | Key Features and Benefits | Max Temperature Resistance (°F) | Durability Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nanotechnology-Based Coatings | Enhanced durability and wear resistance; safer for consumers | Up to 550 | Very High |
| Sol-Gel Coatings | Strong surface bonding; withstands high heat | Up to 500 | High |
| Graphene-Enhanced Coatings | Abrasion resistance and antibacterial properties | N/A | Enhanced |
Multi-layer coatings, such as Durastone, offer improved performance and more choices for consumers. These innovations focus on safety, durability, and better cooking results.
Multi-Layered and Composite Materials
Material selection in 2025 often favors multi-layered and composite designs. Multi-layered pots use several metals to improve heat transfer and maintain even temperatures. Composite bases, such as double-layer designs with a metal core between ceramic layers, help retain heat and save energy. Thick metal bases, especially those made from stainless steel or aluminum, ensure rapid and even heating. The shape and type of the composite base, like flat or double-layer, influence heat conductivity and stability. Careful material selection and engineering in composite pots lead to uniform heat distribution, faster cooking, and better efficiency. Composite pot bottom materials play a key role in these improvements.
Smart Materials and Sensor Integration
Smart materials and sensor integration have changed how multicookers work in 2025. Many pots now include temperature sensors with PID controls for precise cooking. Pressure sensors allow users to set custom pressure levels. Some models feature digital scales for automatic weighing and liquid adjustment. Bluetooth-connected thermometers help monitor meat temperature in real time. Manufacturers use smart materials like stainless steel inner pots, ceramic-coated pots, tempered glass lids, and silicone handles for safety and ease of use.
| Feature Category | Details and Examples |
|---|---|
| Sensor Integrations | Temperature sensors, pressure sensors, digital scales, Bluetooth thermometers |
| Smart Materials | Stainless steel pots, ceramic-coated pots, tempered glass lids, silicone handles |
| Connectivity Options | Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, 5G for remote control and app integration |
| Safety Features | Locking lids, automatic pressure release, overheat protection, dual sealing rings |
| Advanced Technologies | AI recipe planning, edge computing, voice assistant compatibility, modular components, self-cleaning features |
| Example Products | Instant Pot Pro Plus, CHEF iQ Smart Cooker, CHEF iQ Sense Thermometer |
Material selection and composite designs, combined with smart features, help users achieve precise and safe cooking results.
Composite Bottom Design for Precision Cooking

Layered Metal Construction
Composite bottom design uses several layers of metal to improve cooking results. Manufacturers often build multicooker pots with a multi-layer structure. This structure may include stainless steel, aluminum, and iron. Each layer has a specific job. Stainless steel resists corrosion and keeps food safe. Aluminum spreads heat quickly. Iron holds heat well. A three-layer composite base combines these metals for better performance.
A 2mm thick heavy-duty iron inner pot helps balance heat distribution and retention. The stainless steel inner lid surrounds food with heat. This layered metal construction keeps the temperature steady. Food cooks evenly from all sides, not just from the bottom. Composite pot bottom materials help maintain consistent heat. This design improves energy efficiency and cooking performance.
Induction Compatibility and Efficiency
Modern multicookers often use composite bottom design to work with induction cooktops. Induction cooking needs a magnetic layer in the pot. Manufacturers add a stainless steel or iron layer to the composite base. This layer allows the pot to work with induction technology.
Induction-compatible composite pots heat up quickly. They use less energy because the heat goes straight into the pot. Energy efficiency increases when the pot matches the induction cooktop. The composite design also reduces heat loss. This means food cooks faster and uses less power. Many users choose composite pots for their high performance and energy efficiency.
Preventing Hot Spots and Ensuring Even Cooking
Composite bottom design helps prevent hot spots in the pot. Hot spots can burn food or cause uneven cooking. The multi-layer structure spreads heat across the whole surface. Aluminum and iron layers work together to move heat evenly. The stainless steel layer protects the food and keeps flavors pure.
Even heat distribution leads to better performance. Food cooks the same way every time. The composite design also saves energy by using heat more efficiently. Chefs and home cooks trust composite pots for their reliability. The design ensures that every meal comes out just right.
Tip: Choose a multicooker with a composite bottom design for the best energy efficiency and cooking performance. Look for a three-layer composite base for even better results.
Comparing Multicooker Pot Materials for Performance
Heat Response and Control
Different multicooker pot materials respond to heat and pressure in unique ways. Stainless steel pots heat up steadily and maintain temperature well, which helps with precise pressure control. Aluminum pots respond quickly to temperature changes, making them good for recipes that need fast adjustments. Nonstick coatings can sometimes create uneven heating, which affects performance and cooking efficiency. Composite pots with layered metals offer the best energy efficiency and even heat distribution. These designs help prevent hot spots and support consistent pressure throughout the cooking process. Reliable heat response improves performance and ensures food cooks evenly every time.
Maintenance and Cleaning
Proper cleaning keeps multicooker pots safe and maintains their performance. The table below shows the best cleaning methods for each part:
| Component | Material/Type | Recommended Cleaning Method |
|---|---|---|
| Inner Pot | Stainless Steel | Dishwasher-safe; soak in warm, soapy water for stubborn residue before cleaning. |
| Lid | Multi-cooker lid | Dishwasher-safe; remove sealing ring and anti-block shield before washing; dry all parts before reassembly. |
| Sealing Ring | Silicone | Wash thoroughly with warm, soapy water; recommended to have separate rings for savory and sweet dishes. |
| Steam Release & Float Valve | Plastic/Valve parts | Periodically check and clean to prevent blockages. |
| Cooker Base | Electrical base | Wipe with a damp cloth only; never immerse in water or liquids. |
| Condensation Collector | Plastic container | Empty and clean regularly. |
Users should avoid abrasive cleaners to protect nonstick surfaces. Regular cleaning prevents residue buildup and supports long-term safety and energy efficiency.
Safety and Health Considerations
Safety remains a top concern when choosing multicooker pot materials. Stainless steel (300 or 400 series) stands out as a safe, non-toxic option with no detectable lead, cadmium, or mercury in food-contact parts. Nonstick coatings, especially those with PTFE, can release harmful chemicals and pose health risks if damaged. Aluminum in food-contact surfaces may leach into food, increasing the risk of neurological disorders. Ceramic coatings sometimes contain nanoparticles like titanium dioxide, which can disrupt the immune system. Manufacturers follow strict standards and use explosion-proof design features to protect users from pressure-related accidents. Reliable safety features and careful material selection ensure high performance and energy efficiency in every cooking session.
How Design and Materials Enhance Multicooker Pot Performance
Pot Shape and Wall Thickness
Pot shape and wall thickness play a major role in multicooker performance. Manufacturers use round or oval shapes to improve heat flow and reduce cold spots. A well-designed pot allows steam and pressure to move evenly. Thick walls help maintain stable temperatures and prevent warping. Composite construction often combines metals to strengthen the pot and support even heating. A thicker wall can also protect against sudden temperature changes. This design helps food cook evenly and keeps the pot safe for long-term use.
Tip: A pot with a composite base and thick walls will deliver better results for stews, rice, and slow-cooked meals.
Lid and Seal Technology
Lid and seal technology affects safety and cooking quality. A tight-fitting lid keeps pressure inside the pot. Silicone seals prevent leaks and help maintain the right temperature. Some lids use composite materials for extra strength and durability. Advanced design features include locking mechanisms and easy-release valves. These features protect users and improve cooking performance. A good seal also keeps flavors and nutrients inside the pot.
- Silicone rings resist heat and last longer.
- Composite lids add strength and help with pressure control.
- Locking designs prevent accidents and make the pot safer.
Integration with Smart Cooking Features
Smart cooking features work with pot materials to improve user experience. Digital controls, smart thermometers, and preset programs connect with stainless steel, ceramic, and non-stick pots. These combinations allow users to monitor cooking, adjust settings, and get consistent results. Composite pots with smart sensors help control temperature and pressure. Removable and dishwasher-safe pots make cleaning easier. The table below shows how different models use design and materials to boost performance:
| Multicooker Model | Pot Material | Smart Cooking Features | User Experience Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Instant Pot Duo Crisp Ultimate | Stainless Steel | Digital Display | Precise cooking control, easy monitoring, dishwasher-safe |
| Ninja Foodi Smart XL | Non-Stick | Smart Thermometer | Accurate temperature control, easy cleaning, user-friendly |
| Breville Fast Slow Pro | Stainless Steel | Custom Programs | Precision cooking, removable pot for easy maintenance |
| Crock-Pot Express Easy Release | Non-Stick | Easy Release Valve | Simple operation, dishwasher-safe, beginner-friendly |
| GreenPan Elite Multicooker | Ceramic Non-Stick | Digital Controls | Health-focused cooking, easy cleaning |
Smart features and composite materials work together to make cooking safer, faster, and more reliable. Users enjoy better performance and less stress in the kitchen.
Choosing the Best Multicooker Pot in 2025
Key Features to Look For
When selecting a multicooker pot in 2025, buyers should focus on features that improve both performance and user experience. Material selection stands out as the most important factor. A high-quality pot ensures even heat and long-lasting use. Stainless steel inserts last longer than nonstick coatings and keep food tasting fresh. Power wattage, usually between 1,000 and 1,500 watts, affects how quickly the pot cooks meals. Clear touch controls and easy programming make the multicooker pot simple to use. Multifunctionality, such as air-frying or dehydrating, adds value. Some models let users monitor food while steaming, which helps control the cooking process. Taste and tenderness of food show the true quality of the pot.
Tip: Look for a multicooker pot with a durable interior, smart controls, and multiple cooking modes for the best results.
Matching Material to Cooking Style
Material selection should match the way a person likes to cook. Stainless steel works well for those who want durability and pure flavors. Nonstick coatings suit users who prefer easy cleanup, but they may not last as long. Anodized aluminum heats up fast and fits busy kitchens. Composite pots with layered metals give the best heat distribution and energy savings. Material selection also affects how the pot handles pressure and temperature changes. People who cook stews or rice often should choose thicker walls and a composite base for better quality. Material selection shapes the cooking experience and the final taste of each meal.
| Cooking Style | Best Material Selection | Why It Works Well |
|---|---|---|
| Slow Cooking | Stainless Steel, Composite | Even heat, strong, pure flavor |
| Quick Meals | Anodized Aluminum, Nonstick | Fast heating, easy cleaning |
| Multi-Function | Composite, Layered Metals | Versatile, energy efficient |
Practical Tips for Buyers
Buyers can avoid common mistakes by learning about material selection and pot design. They should know the difference between a multicooker pot and a stovetop pressure cooker. Size matters; a pot like the T-Fal Trendy can work as both a 4-quart and 6-quart cooker. Multiple pressure settings help prevent overcooking. Cleaning ease is important, as some pots are bulky. An extra inner pot can speed up meal prep and storage. Reliable models, such as the Instant Pot Duo, offer proven quality. Adjusting recipes for different pots may require changing liquid amounts. Paying attention to pressure release methods can prevent messy spills.
Note: Careful material selection and attention to quality help buyers get the most from their multicooker pot.
Selecting the right multicooker pot material shapes cooking results in modern kitchens. Stainless steel and nonstick pots each offer unique benefits. The table below shows expert recommendations:
| Pot Material | Precision & Heating | Safety Considerations | Efficiency & Maintenance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Heats evenly, durable | Safe with utensils, harder to clean | Long-lasting, more cleaning |
| Nonstick | Less even heating | Coating scratches easily | Easy to clean, handle with care |
Innovations in 2025 give home cooks more choices for safe, efficient, and precise cooking.
FAQ
What is the safest material for multicooker pots in 2025?
Stainless steel offers the highest safety. It resists corrosion, does not react with food, and meets international food safety standards.
How does composite bottom design improve cooking results?
Composite bottom design spreads heat evenly. It prevents hot spots and helps food cook consistently. Energy efficiency increases with layered metals.
Can smart sensors in multicooker pots help prevent overcooking?
Smart sensors monitor temperature and pressure. They adjust cooking time automatically. Users get better results and avoid overcooked meals.


